Binary <==> Decimal Conversion
- Jun 3, 2020
- 1 min read
Binary to Decimal Conversion of numbers uses weighted columns to identify the order of the digits to determine the final value of the number => https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/binary/bin_2.html
For example,
1011 = 1*2^3 + 0*2^2 + 1*2^1 + 1*2^0 = 8+0+2+1 = 11
1000= 1*2^3 + 0*2^2 + 0*2^1 + 0*2^0 = 8+0+0+0 = 8
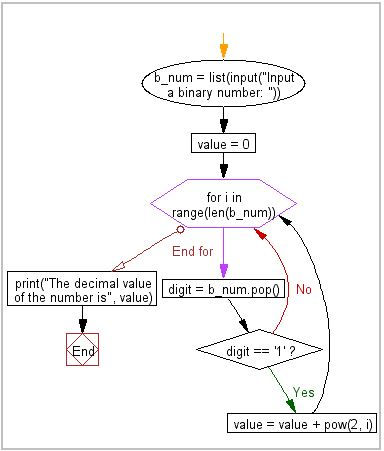
In Python, there is a trick when we print converted binary to decimal, the trick is add Prefix 0b (0 is zero) before the binary:
print(0b1011) => 11
print(0b1000) => 8
print(0b1011000) => 88
For octal, the prefix is 0o. For hexadecimal, the prefix is 0x.
Now, what about the other way around? convert decimal to binary?
The answer is to use bin() function => https://www.w3resource.com/python/built-in-function/bin.php
so try,
print(bin(11)),
print(bin(8)),
print(bin(88))
To convert to octal, using oct() function.
To convert to hexadecimal, using hex() function.
A more explicit way for the conversion is to use int() function, the syntax is
int(x, base)
=> https://www.w3resource.com/python/built-in-function/int.php. But there are several things we need to know.
First, x can be a number or a string. In our case, in fact, it has to be string, as when we convert, we need to put prefix0b all together into parenthesis. And "b" is a letter.
Second, base is Number format. Default value is 10, which is decimal. In our case, the base should be 2, as it is binary.
so try,
print(int("0b1001111",2)) => 79
print(int("0b1011",2)) => 11
In the same way, we can convert octal and hexadecimal.
Sejal Jaiswal wrote a very good article for Python Data Type Conversion => https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/python-data-type-conversion








Comments